По данным Всемирной ядерной ассоциации, гигаватт мощности, произведенной на угольных станциях, обходился в 342 жертвы, на газовых — в 85, на гидростанциях — в 885, тогда как на атомных — всего в 8.
Ниже - собственно данные World Nuclear Association - WNA
" ...Safety relative to other energy sources
Many occupational accident statistics have been generated over the last 40 years of nuclear reactor operations in the US and UK. These can be compared with those from coal-fired power generation. All show that nuclear is a distinctly safer way to produce electricity.
Deaths from energy-related accidents per unit of electricity
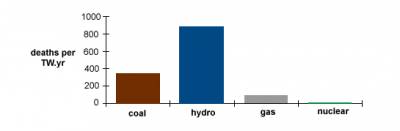
Source: Paul Scherrer Institut 1998, considering 1943 accidents with more than five fatalities.
One TW.yr is the amount of electricity used by the world in about five months.
Coal-fired power generation has chronic, rather than acute, safety implications for public health. It also has profound safety implications for the mining of coal, with thousands of workers killed each year in coal mines (see Appendix).
Coal-fired power generation has chronic, rather than acute, safety implications for public health. It also has profound safety implications for the mining of coal, with thousands of workers killed each year in coal mines (see Appendix).
Hydro power generation has a record of few but very major events causing thousands of deaths. In 1975 when the Banqiao, Shimantan & other dams collapsed in Henan, China, at least 30,000 people were killed immediately and some 230,000 overall, with 18 GWe lost. In 1979 and 1980 in India some 3500 were killed by two hydro-electric dam failures, and in 2009 in Russia 75 were killed by a hydro power plant turbine disintegration.
Three simple sets of figures are quoted in the Tables below and that in the appendix. A major reason for coal's unfavourable showing is the huge amount which must be mined and transported to supply even a single large power station. Mining and multiple handling of so much material of any kind involves hazards, and these are reflected in the statistics.
Summary of severe* accidents in energy chains for electricity 1969-2000
| |
OECD |
|
Non-OECD |
|
| Energy chain |
Fatalities |
Fatalities/TWy |
Fatalities |
Fatalities/TWy |
| Coal |
2259 |
157 |
18,000 |
597 |
| Natural gas |
1043 |
85 |
1000 |
111 |
| Hydro |
14 |
3 |
30,000 |
10,285 |
| Nuclear |
0 |
0 |
31 |
48 |
Data from Paul Scherrer Institut, in OECD 2010. * severe = more than five fatalities
Comparison of accident statistics in primary energy production
(Electricity generation accounts for about 40% of total primary energy)
| Fuel |
Immediate fatalities
1970-92 |
Who? |
Normalised to deaths
per TWy* electricity |
| Coal |
6400
|
workers
|
342
|
| Natural gas |
1200
|
workers & public
|
85
|
| Hydro |
4000
|
public
|
883
|
| Nuclear |
31
|
workers
|
8
|
* Basis: per million MWe operating for one year, not including plant construction, based on historic data which is unlikely to represent current safety levels in any of the industries concerned.
Sources: Sources: Ball, Roberts & Simpson, 1994; Hirschberg et al, Paul Scherrer Institut 1996, in: IAEA 1997; Paul Scherrer Institut, 2001.
In the UK, Friends of the Earth commissioned a study by the Tyndall Centre, which drew primarily on peer-reviewed academic literature, supplemented by literature from credible government, consultancy and policy sources. It concluded in January 2013 that “Overall the safety risks associated with nuclear power appear to be more in line with lifecycle impacts from renewable energy technologies, and significantly lower than for coal and natural gas per MWh of supplied energy.”
Источники:
http://www.vedomosti.ru/newspaper/article/259219/strashnaya_bezopasnost
http://www.world-nuclear.org/info/Safety-and-Security/Safety-of-Plants/Safety-of-Nuclear-Power-Reactors/
Comparing Nuclear Accident Risks with Those from Other Energy Sources
English, 52 pages, published: 08/31/10
NEA#6861, ISBN: 978-92-64-99122-4
http://www.oecd-nea.org/tools/publication?div=NDD&period=100y&sort=title&filter=1#p6861
Источник: http://www.world-nuclear.org/info/Safety-and-Security/Safety-of-Plants/Safety-of-Nuclear-Power-Reactors/ |